Data mining is everywhere, but its story starts many years before Moneyball and Edward Snowden. The following are major milestones and “firsts” in the history of data mining plus how it’s evolved and blended with data science and big data.
Data mining is the computational process of exploring and uncovering patterns in large data sets a.k.a. Big Data. It’s a subfield of computer science which blends many techniques from statistics, data science, database theory and machine learning.
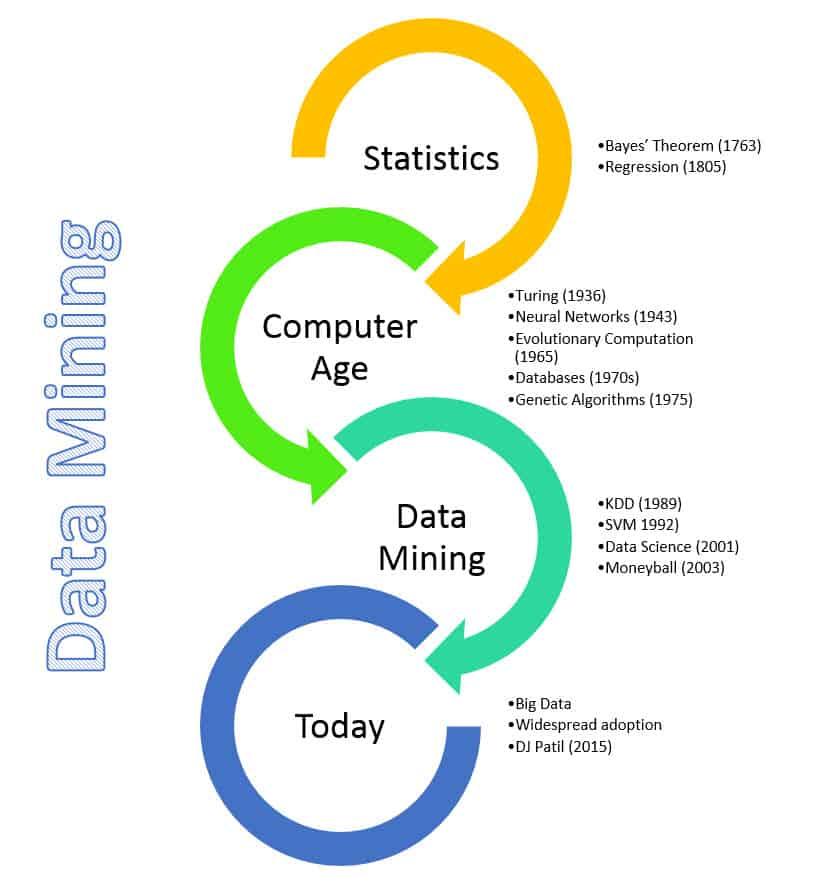
1763 Thomas Bayes’ paper is published posthumously regarding a theorem for relating current probability to prior probability called the Bayes’ theorem. It is fundamental to data mining and probability, since it allows understanding of complex realities based on estimated probabilities.
1805 Adrien-Marie Legendre and Carl Friedrich Gauss apply regression to determine the orbits of bodies about the Sun (comets and planets). The goal of regression analysis is to estimate the relationships among variables, and the specific method they used in this case is the method of least squares. Regression is one of key tools in data mining.
1936 This is the dawn of computer age which makes possible the collection and processing of large amounts of data. In a 1936 paper, On Computable Numbers, Alan Turing introduced the idea of a Universal Machine capable of performing computations like our modern day computers. The modern day computer is built on the concepts pioneered by Turing.
1943 Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts were the first to create a conceptual model of a neural network. In a paper entitled A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity, they describe the idea of a neuron in a network. Each of these neurons can do 3 things: receive inputs, process inputs and generate output.
1965 Lawrence J. Fogel formed a new company called Decision Science, Inc. for applications of evolutionary programming. It was the first company specifically applying evolutionary computation to solve real-world problems.
1970s With sophisticated database management systems, it’s possible to store and query terabytes and petabytes of data. In addition, data warehouses allow users to move from a transaction-oriented way of thinking to a more analytical way of viewing the data. However, extracting sophisticated insights from these data warehouses of multidimensional models is very limited.
1975 John Henry Holland wrote Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems, the ground-breaking book on genetic algorithms. It is the book that initiated this field of study, presenting the theoretical foundations and exploring applications.
1980s HNC trademarks the phrase “database mining.” The trademark was meant to protect a product called DataBase Mining Workstation. It was a general purpose tool for building neural network models and now no longer is available. It’s also during this period that sophisticated algorithms can “learn” relationships from data that allow subject matter experts to reason about what the relationships mean.
1989 The term “Knowledge Discovery in Databases” (KDD) is coined by Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro. It also at this time that he co-founds the first workshop also named KDD.
1990s The term “data mining” appeared in the database community. Retail companies and the financial community are using data mining to analyze data and recognize trends to increase their customer base, predict fluctuations in interest rates, stock prices, customer demand.
1992 Bernhard E. Boser, Isabelle M. Guyon and Vladimir N. Vapnik suggested an improvement on the original support vector machine which allows for the creation of nonlinear classifiers. Support vector machines are a supervised learning approach that analyzes data and recognizes patterns used for classification and regression analysis.
1993 Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro starts the newsletter Knowledge Discovery Nuggets (KDnuggets). It was originally meant to connect researchers who attended the KDD workshop. However, KDnuggets.com seems to have a much wider audience now.
2001 Although the term data science has existed since 1960s, it wasn’t until 2001 that William S. Cleveland introduced it as an independent discipline. As per Build Data Science Teams, DJ Patil and Jeff Hammerbacher then used the term to describe their roles at LinkedIn and Facebook.
2003 Moneyball, by Michael Lewis, is published and changed the way many major league front offices do business. The Oakland Athletics used a statistical, data-driven approach to select for qualities in players that were undervalued and cheaper to obtain. In this manner, they successfully assembled a team that brought them to the 2002 and 2003 playoffs with 1/3 the payroll.
Present In February 2015, DJ Patil became the first Chief Data Scientist at the White House. Today, data mining is widespread in business, science, engineering and medicine just to name a few. Mining of credit card transactions, stock market movements, national security, genome sequencing and clinical trials are just the tip of the iceberg for data mining applications. Terms like Big Data are now commonplace with the collection of data becoming cheaper and the proliferation of devices capable of collecting data.
This content originally appeared on http://rayli.net/blog/
Like this article? Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to never miss out!






