Deep learning (DL) is the discipline of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on intelligent machines’ learning and comprehension ability. Deep learning models are designed inspired by the structure and working principle of the human brain. DL is a critical technology that makes intuitive autonomous systems a reality and generally aims to create machines able to think and feel.
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
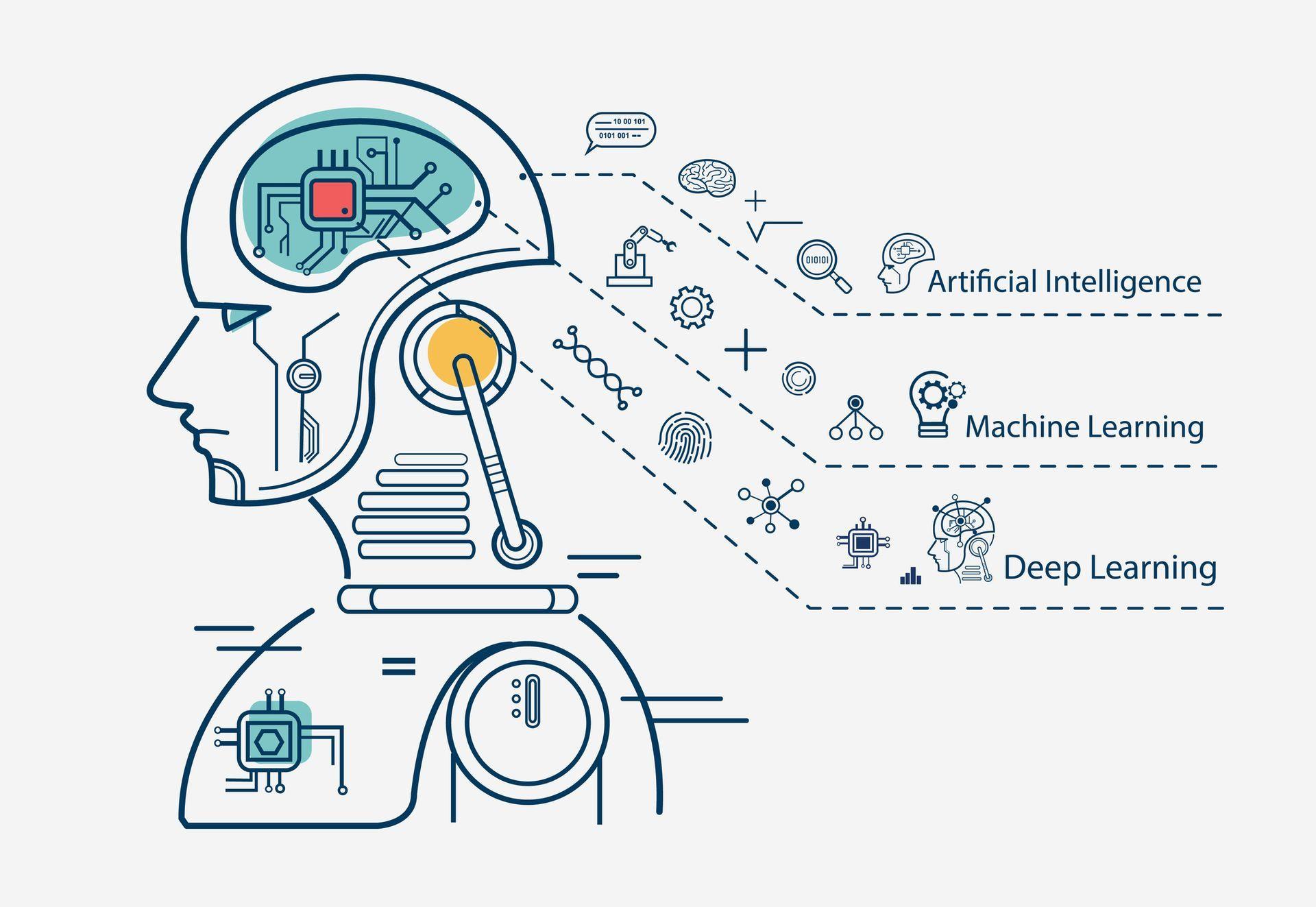
Deep learning is a sub-branch of machine learning (ML) that mimics the functioning of the human brain during data processing. It allows machines to learn without human supervision. It gives the ability to understand spoken words and what’s behind them, translate, identify objects and make informed decisions.
Despite being a branch of machine learning, DL systems do not have limited learning capabilities like traditional ML algorithms. Instead, DL systems can continually improve their abilities beyond imagination as they are fed larger and more consistent data.,
Unstructured big data is nearly impossible for the feeble human mind to process. Finding important information in massive datasets may take years, even if you have the resources. DL has made this task extremely easy for machines.
DL is a type of machine learning that uses artificial intelligence to learn and improve on its own. Deep learning also enables computers to acquire knowledge from unlabeled and unstructured data.

What is an artificial neural network?
The ability of AI systems to mimic human learning is made possible by deep learning. DL algorithms seek to conclude by analyzing data every once in a while. To achieve this, artificial neural networks (ANNs) are used, an electronic replica of the human brain. Artificial neural networks aim to give machines human qualities such as problem-solving abilities, self-awareness, sight, creativity, and empathy.
The widespread availability of computers, faster and more powerful processors, and smaller storage devices have made deep learning a reality. The same may be said for storage devices, as a significant amount of data must be stored and processed to make DL a reality. Because of this, DL research has been in hibernation for decades. The first practical applications of deep learning predicted in the 1980s had to wait until now.
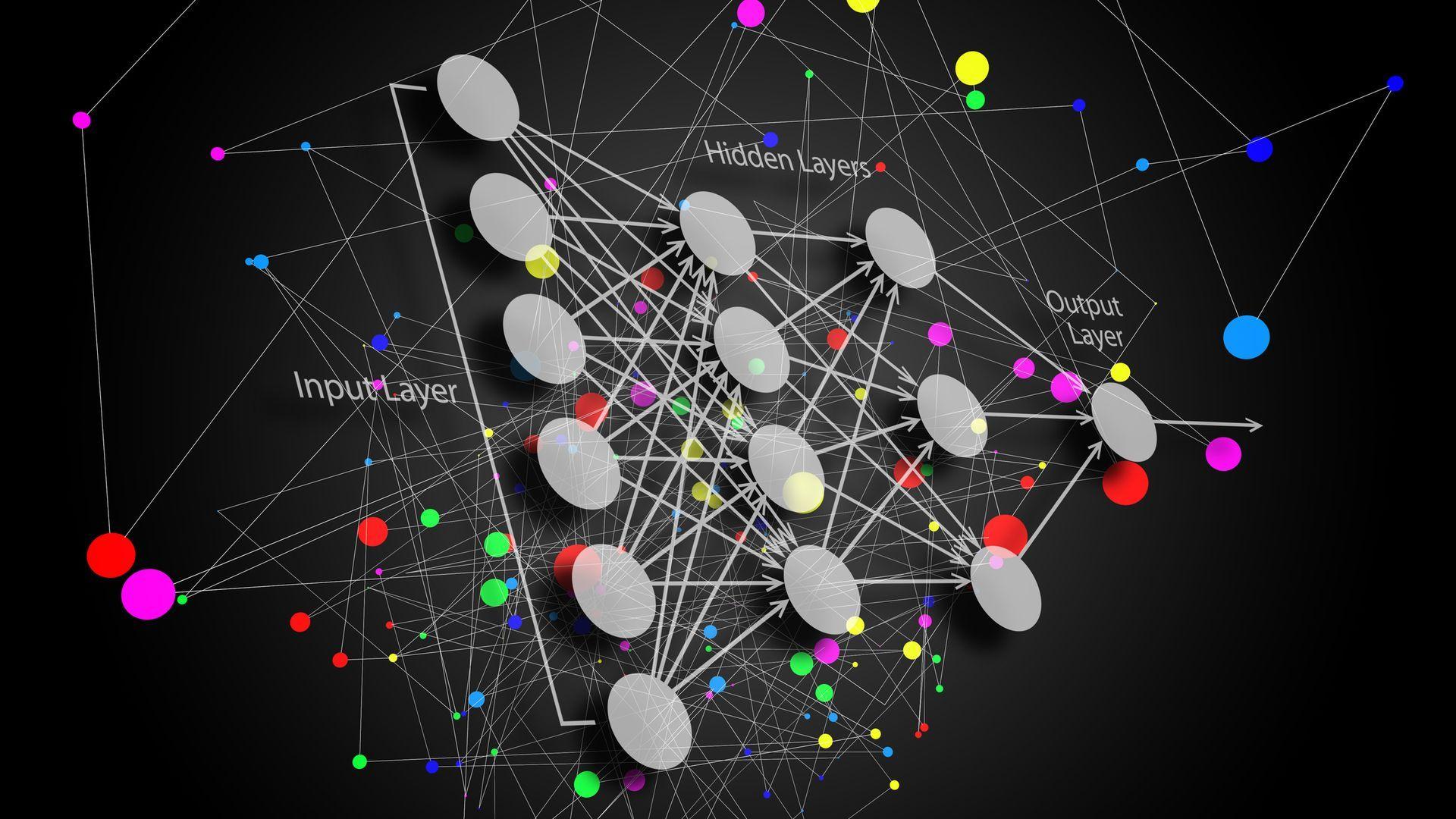
How does deep learning work?
The training procedure in deep learning adjusts the system behaviors dependent on the feedback loop. Every correct action has a reward. The system attempts to maximize the reward by improving its behavior.
Artificial neural networks are the backbone of deep learning. These, like human brain neurons, are based on artificial neural networks. Artificial neural networks are made up of numerous sensors that act in place of real neurons. The number of hidden layers in a neural network is called “deep.” Traditional neural networks have two to three hidden layers, while deep networks can include up to 150.
Another approach to grasping the way deep learning works is to look at Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Convolutional neural networks use convolution, which allows them to identify features without requiring manual data labeling. None of the attributes are taught to the machine; instead, it learns from a set of pictures. Deep learning models’ automatic attribute detection ability makes them advantageous for classifying items and other computer vision activities.
The hundreds of layers in deep neural networks make them extremely sensitive to features and image classification. The complexity of the learned picture features changes directly as the number of layers increases, owing to each layer learning to describe certain characteristics.
DL vs. ML: Differences between deep learning and machine learning
Machine learning
The term “machine learning” refers to the application of artificial intelligence (AI) to teach computers how to accomplish tasks they were not originally programmed for through trial and error, allowing them to improve their performance.
Spam filters in your email account, for example, are machine learning technologies in action. ML algorithms are also used on services like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify to recommend material you’ll enjoy based on your past preferences.
Machine learning algorithms can perform various tasks such as analyzing data, finding patterns, and making predictions. They learn and adapt as they are given new information. With the possibility to learn and grow, machine learning humanizes computers.
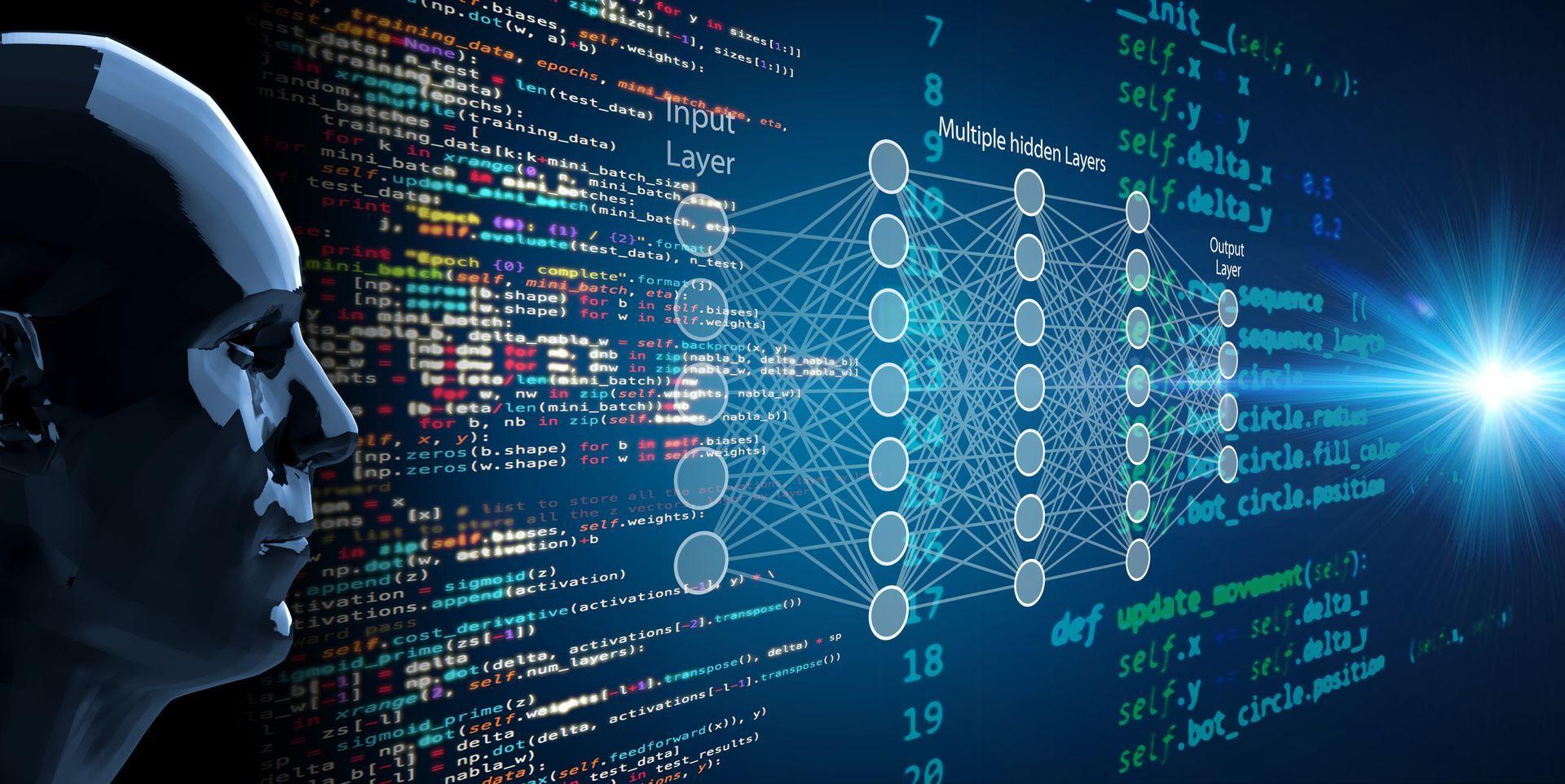

Deep learning
Deep learning is a more advanced form of machine learning. While machine-learning algorithms may learn and develop gradually, they require some assistance. Human involvement, for example, is required when the algorithm makes an incorrect prediction. Artificial neural networks are the key to the learning process for deep machine learning. They allow deep machine learning algorithms to learn on their own, whether or not their predictions are accurate, with the help of artificial neural networks.
Another method to tell the difference between machine learning and deep learning is to assess how they learn. Let’s assume you’re attempting to teach a computer to distinguish dog and cat photos. If you’re utilizing a machine learning algorithm, it must be fed with structured data to recognize certain features that differentiate the dogs and cats in the photographs. Each picture is given a name, which the algorithm uses to distinguish between the two species better. The deep learning method does not require structured data or labeled pictures; simply raw information. Artificial neural networks enable algorithms to identify and comprehend each animal’s various features.
Deep learning systems may require weeks or months to train, but a machine learning system might be trained in mere minutes or hours
The deep learning system creates unique categories to describe animals and pictures after processing the images through several layers of deep neural networks. The various outputs generated by each neural network layer are combined in the next step to classify the images correctly.
Another distinction between machine learning and deep learning is the requirement for hardware. Due to the simplicity of the computations and data handled, machine learning algorithms require less computing power. As a result, ML applications may be run on little or no computational resources. On the other hand, deep learning systems need a great deal of computational power and graphical processing units (GPUs). GPUs may improve the performance of deep learning systems by a factor of 100 or more.
The amount of time it takes to teach deep learning and machine learning algorithms varies. As you may guess, deep learning methods take time to train since they require huge data and sophisticated computations. Deep learning systems may require many hours or weeks to train, but a machine learning system might be trained in seconds or hours.

The current state of deep learning
Today, Deep Learning technologies are used in business and our daily lives, mostly without anyone being aware.
For example, map applications use current and historical traffic data to compute the average travel time. They also consider people’s preferred routes when calculating this statistic. AI-powered voice assistants are getting better at better understanding spoken words. They answer your questions and execute the responsibilities you’ve given them.
Your preferences and even what you write on applications and websites are used to determine what content is more suitable for you at any minute, and it is provided to you.
In the cyber security sector, one of the greatest uses for Deep Learning is evident. Early warning and proactive action can be provided by deep learning, which can recognize patterns of potentially dangerous software, applications, and websites as well as cyber-attacks.






