Regardless of how big or small the company is, data lifecycle management is a fundamental discipline. Data is now everywhere. Furthermore, everything is interrelated. The same body of information is distributed among many departments and employees at any organization. Corporate data has evolved into a unified, living entity that permeates all information systems.
What is the data life cycle?
The entire time that data is present in your system is referred to as the data life cycle, also known as the information life cycle. This life cycle includes every stage your data experiences, starting with the first capture and continuing on.
Each stage of life, according to life science, includes childhood, a time of growth and development, productive adulthood, and old age. These stages change as you move up the tree of life. While whales live to be grandmothers, salmon perish shortly after spawning. A mouse’s, a fox’s, and a butterfly’s life cycles will all be highly dissimilar even though they all inhabit the same field.
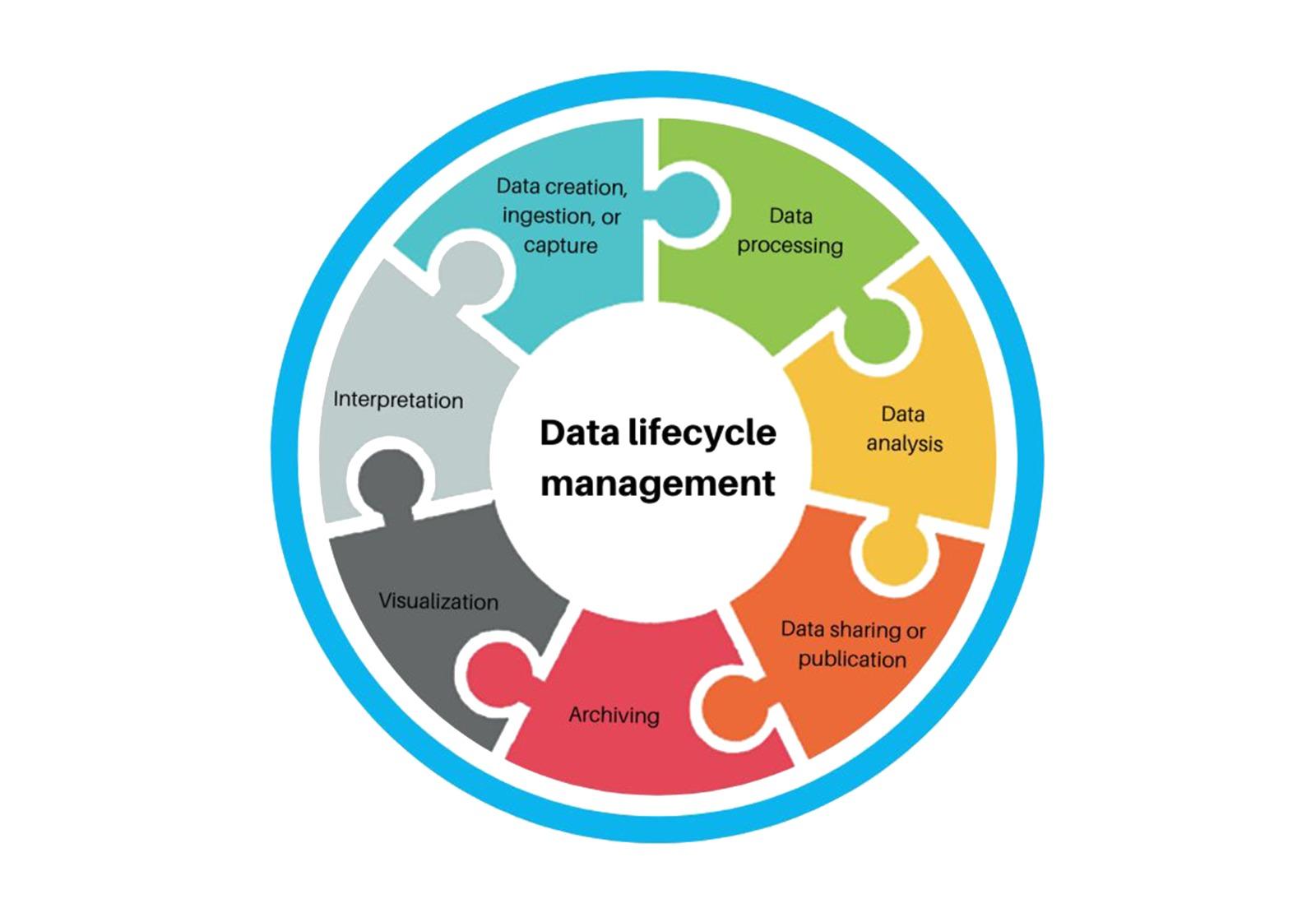
Data lifecycle framework: 7 data lifecycle stages
The DLM architecture has several variations because each organization has its own business model, software stack, and sorts of data.
Similar to how distinct data objects experience different life stages at their own cadences. Having stated that here is a sample data lifecycle framework:
Data creation, ingestion, or capture
You obtain information in some way, whether you create data through data entry, obtain pre-existing data from other sources, or take in signals from equipment. This phase explains when data values enter your system’s firewalls.
Data processing
Cleaning and processing raw data for further analysis involve a number of steps. Data preparation often entails combining data from several sources, validating the data, and executing the transformation, though the exact order of processes may vary. The data processing pipeline frequently includes the reformatting, summarizing, subsetting, standardizing, and enhancing of data.
Data analysis
Regardless of how you examine and interpret your data, this is the crucial stage. A number of analyses might be necessary for exploring and analyzing your data. This could refer to visualization and statistical analysis. It might also refer to utilizing artificial intelligence or conventional data modeling (AI).

Data sharing or publication
Forecasts and insights are transformed into decisions and direction at this level. Your data offers its full commercial value when you share the knowledge you learned from data analysis.
Archiving
Normally, data is saved for later use once it has been gathered, handled, analyzed, and shared. It’s crucial to preserve metadata about each item in your records, especially regarding data provenance, if you want archives to retain any value in the future.
Visualization
The act of developing graphic representations of your data is known as data visualization, and it is often carried out with the aid of one or more visualization tools. By using data visualization, you may more easily explain your study to a larger audience both inside and outside of your company. Your visualization’s format will rely on the data you’re using and the narrative you wish to convey.

Data visualization has grown in importance throughout the data life cycle, despite the fact that it isn’t technically a step that must be taken for every data project.
Interpretation
Finally, you can make meaning of your analysis and visualization during the interpretation phase of the data life cycle. This is the time to do more with the data than just deliver it; instead, you should investigate it using your knowledge and insight. In addition to describing or explaining what the data indicates, your interpretation may also contain potential ramifications.
What is Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)?
By combining a business and technical approach, Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) enhances database development (or acquisition), delivery, and management.
As an abstract idea, the data life cycle serves no one. Its goal is to assist companies in providing end-users with the data health they require to support decisions. Data lifecycle management must be open and iterative in order to achieve this.
Document the movement of data across your company with a data lineage map to make its life cycle real. This entails graphically illustrating the starting point of your data, each stop it makes, and an explanation of why it might not have moved at that particular time. Documenting the life cycle of a process makes tracking for routine data operations easier. Additionally, it makes it simple to identify and fix failure locations and bottlenecks.
Processes that reduce the data’s usefulness are counterproductive and should be identified and changed in subsequent cycles. Utilize the knowledge gained throughout the process to guide the following cycle and improve data health.
For businesses, the data sharing stage is frequently difficult. A top-down strategy with tightly restricted data access does not scale up well. Gatekeeper-based data infrastructure leads to scenarios where IT is overloaded with requests and end-users struggle to receive the data they require in a timely manner. On the other side, it is challenging to ensure the security and privacy of sensitive data when using a bottom-up strategy with open access to all data. End-users receive only the data they require when they require it thanks to data governance.
Data lifecycle diagram
We can visualize the diagram such as:
Data Lifecycle Management’s three main goals
The basis of contemporary business is data. Consequently, a strong data lifecycle management strategy is necessary to guarantee its security, availability, and dependability. The necessity for proper data management is higher than ever due to the exponential growth of data.
DLM’s three key objectives are confidentiality, integrity, and availability to enable smooth information flow throughout its lifecycle.
Confidentiality
Huge amounts of data are used and shared daily by organizations. This raises the possibility of data loss and information misuse. In order to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks, such as financial records, business plans, personally identifiable information (PII), etc., data security and confidentiality are essential.
Integrity
Data is accessed, used, and shared by several users after it is stored in an organization’s storage systems. Any time a piece of data is used, it will inevitably go through several adjustments. The accuracy, reliability, and currentness of the information made available to users must be guaranteed by an organization’s DLM strategy. Therefore, preserving data integrity by safeguarding the data while it is being used, transported, and stored is one of the objectives of a DLM strategy.
Availability
Although data security and integrity are crucial, they wouldn’t be much use if they weren’t accessible to users when they needed them. In today’s 24/7 global corporate world, data availability is particularly important. DLM seeks to guarantee that data is accessible and available to users when they need it, preventing interruptions to crucial business operations.
Why is the data life cycle important?
Understanding the data life cycle can help you communicate more successfully with individuals who do work directly with your organization’s data team or projects. Additionally, it might give you insights that help you come up with ideas for prospective projects or efforts. It has serious benefits.

DLM assists you in maximizing the use of your data up until the point at which it is removed by defining, organizing, and developing policies around how data should be managed at each stage of its existence.
Data Lifecycle Management benefits
Apart from streamlining the flow of information and optimizing data throughout its lifecycle, a DLM offers several other benefits.
Compliance
Organizations are required by some industry compliance standards to keep data for a specific amount of time. For instance, the Security Policy for the Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS) says that the “agency shall maintain audit documents for at least one year. The agency must keep audit records after the minimum retention period has passed until it is decided they are no longer required for administrative, legal, audit, or other operational objectives. While also addressing additional requirements like audit, legal, and investigations, DLM assists organizations in adhering to rules (both local and regional).
Data governance
Data is used by organizations to enhance corporate operations and make wise decisions. In accordance with data privacy laws, a good data lifecycle management plan helps to ensure that data is consistently available, consistent, reliable, and safe.
If you wonder what is data governance and want to learn the best data governance practices, go to these articles.
Data protection
Data security is the top issue for both company leaders and IT workers given the threat landscape of today. DLM aids businesses in defending their data against theft, deletion, cyberattacks, and other threats. Businesses can specify how their data is handled, used, kept, and shared thanks to this. This reduces the possibility of data breaches and guards against the exploitation of sensitive information.

Value and efficiency
Today’s businesses are data-driven. An organization’s strategic initiatives are heavily reliant on data. As a result, it’s critical for businesses to make sure their data is accurate, current, and authentic. A sound DLM strategy makes sure that the data users have access to is accurate and trustworthy, allowing organizations to get the most value out of their data. DLM aids in preserving data quality throughout its lifecycle, allowing for process improvement and boosting productivity.
How can Data Lifecycle Management help small businesses?
The advantages of DLM may often be applied to smaller businesses as well. If you’re managing a very small organization, creating and executing all these policies and automated procedures could seem excessive. But it’s never too early to think about the DLM stages and develop a data management strategy that can scale with your business.
Small businesses often fail to properly file away “small” documents, allowing them to disappear through the cracks and potentially causing lost or destroyed files or data to get into the wrong hands.

Your organization will be able to handle the data safely and effectively from the point of creation to the point of deletion with the correct data lifecycle management methods and strategy.
For the various stages of DLM, you can think about doing the following things on a smaller scale:
- Collection
- Data storage
- For data maintenance
- For data usage
- Data cleaning
Best data management tools (2022)
Are you searching for the best data management tools for 2022? Let’s look at a few of the top tools from each category now that you’ve seen the different types of data management solutions. These solutions could be a fantastic addition to your pipeline for enterprise workflow.
ETL and data integration tools
In computers, the process of copying data from many sources into a system that represents the data is known as extracting, transforming, and loading. On the other side, data integration describes the procedure of merging data from various sources into a single destination.
These are some of the best ETL and data integration tools:
Cloud data management tools
The availability of off-premise options for data warehousing and management has increased significantly since storage and bandwidth become more affordable. Businesses that must store, analyze, and sort through a lot of data have embraced cloud-based solutions to increase productivity. The development of powerful Cloud Data Management Tools over the past five to ten years has made this possible. However, with the development of technology, many smaller businesses are now providing tools for consumers with data demands of all kinds. Although these industries are still predominantly controlled by industry giants like Google and Amazon. Here are three of the most important tools in this area.
These are some of the best cloud data management tools:
Master data management tools
Utilizing master data management tools, you may combine all of the enterprise’s business applications from several departments into a single file. Here are a few master data management tools that might assist you in establishing a single point of contact for your company.
These are some of the best master data management tools:
Data visualization and data analytics tools
With the help of data visualization tools, you may display your data in a visual format (such as graphs and charts), which makes it simpler to derive meaningful conclusions from it and streamline the analytical process. Here are some useful tools for data analytics and visualization that you may use into your business model.
These are some of the best data visualization and data analytics tools:
Data management challenges
Data management presents its own set of difficulties. The ever-growing amount of data is typically the cause of data management issues. The following is a list of challenges that organizations may have while attempting to integrate data management tools into their workflow:
Uncertain goals and objectives
One of the major problems with data management is that it is unclear what an organization expects from the processed data. The full potential of the Data Management Tools cannot be realized in the absence of a clear objective for gathering the appropriate data and analyzing it to support data-driven business choices.
Meeting regulatory standards
In order to comply with the continuously evolving compliance standards, organizations must frequently evaluate their data and procedures to make sure that everything is in line with the latest or newer requirements.

Multiple data storage options
Data is stored using a variety of platforms, making analysis challenging because there isn’t a single format or source for it. Therefore, in order to facilitate easier analysis, data must be translated into a consistent format.
Sparse usage of data management
Companies find it difficult to properly comprehend the location, volume, and use of the enterprise’s data due to the enormous amount of data that must be accounted for.
Extracting value that addresses
The biggest difficulty is making sense of data gathered from many sources. To get the most value out of data in the form of practical insights, it is important to comprehend how data management and analytics work together.
Conclusion
In order to make data manageable and accessible, databases were developed in the 1980s; nevertheless, these databases also brought new issues for gathering, storing, protecting, and erasing data. Data Lifecycle Management is a concept that has been developed through time by data and IT experts via theorizing and exchanging best practices (DLM).
The volume and complexity of your data will rise as your firm expands. You may view the whole route of your data across the enterprise by building a framework based on DLM, regardless of the size of your business or the IT infrastructure you manage.
Any organization, from large corporations to small and medium-sized enterprises, can create a structure for their data to flow through or update an existing one by understanding the DLM concepts.
Remember that there are goals and benefits, but there are also some challenges. You should carefully review the tools and select the one that best fits your needs.






