Google Muse AI is the latest additon from the tech giant to a swarm of AI tools we have been seeing lately. The new text-to-image transformer model claims to be quicker than competing methods, because it uses parallel decoding and a compact, discrete latent space. According to its developers, Google Muse AI can produce images at state-of-the-art image generation performance.
We present Muse, a text-to-image Transformer model that achieves state-of-the-art image generation performance while being significantly more efficient than diffusion or autoregressive models.
Google Muse AI team
What is Google Muse AI?
Google Muse AI is an allegedly improved version of earlier text-to-image transformer models like Imagen and DALL-E 2. Muse is trained on a masked modeling task in discrete token space using the text embedding acquired from a pre-trained large language model (LLM).

Muse has been trained to identify tokens in images that have been arbitrarily obscured. Muse claims to outperform pixel-space diffusion models like Imagen and DALL-E 2 due to its usage of discrete tokens and smaller sample size requirements. Iteratively resampling picture tokens based on a text prompt, the model produces a free zero-shot, mask-free editing.
When compared to other models, Muse has faster inference times, according to MUSE.
| Model | Resolution | Inference Time (↓) |
| Stable Diffusion 1.4 | 512×512 | 3.7s |
| Parti-3B | 256×256 | 6.4s |
| Imagen | 256×256 | 9.1s |
| Imagen | 1024×1024 | 13.3s |
| Muse-3B | 256×256 | 0.5s |
| Muse-3B | 512×512 | 1.3s |
Muse employs parallel decoding, which is missing from Parti and other autoregressive models. With an LLM that has already been trained, it is possible to grasp language at a granular level, which in turn translates to producing high-quality images and recognizing visual concepts like objects, their spatial relationships, stance, cardinality, and so on. Further, Muse allows for inpainting, outpainting, and mask-free editing without having to flip or flip the model.

Check out the best free AI art generators
Google Muse AI features
Muse is a fast, state-of-the-art text-to-image generation and editing model that has so much to offer:
- Text-to-image generation
- Google Muse AI quickly produces high-quality images in response to textual inputs (1.3s for 512×512 resolution or 0.5s for 256×256 resolution on TPUv4).

- Zero-shot, mask-free editing
- Due to the iterative resampling of picture tokens based on a text prompt, the Google Muse AI model provides us with free zero-shot, mask-free editing.

- When altering an image, mask-free editing allows you to manipulate several objects with a simple text prompt.

- Zero-shot Inpainting/Outpainting
- Mask-based editing (inpainting/outpainting) is included for free in Google Muse AI. When using a mask, editing is the same as a generation.
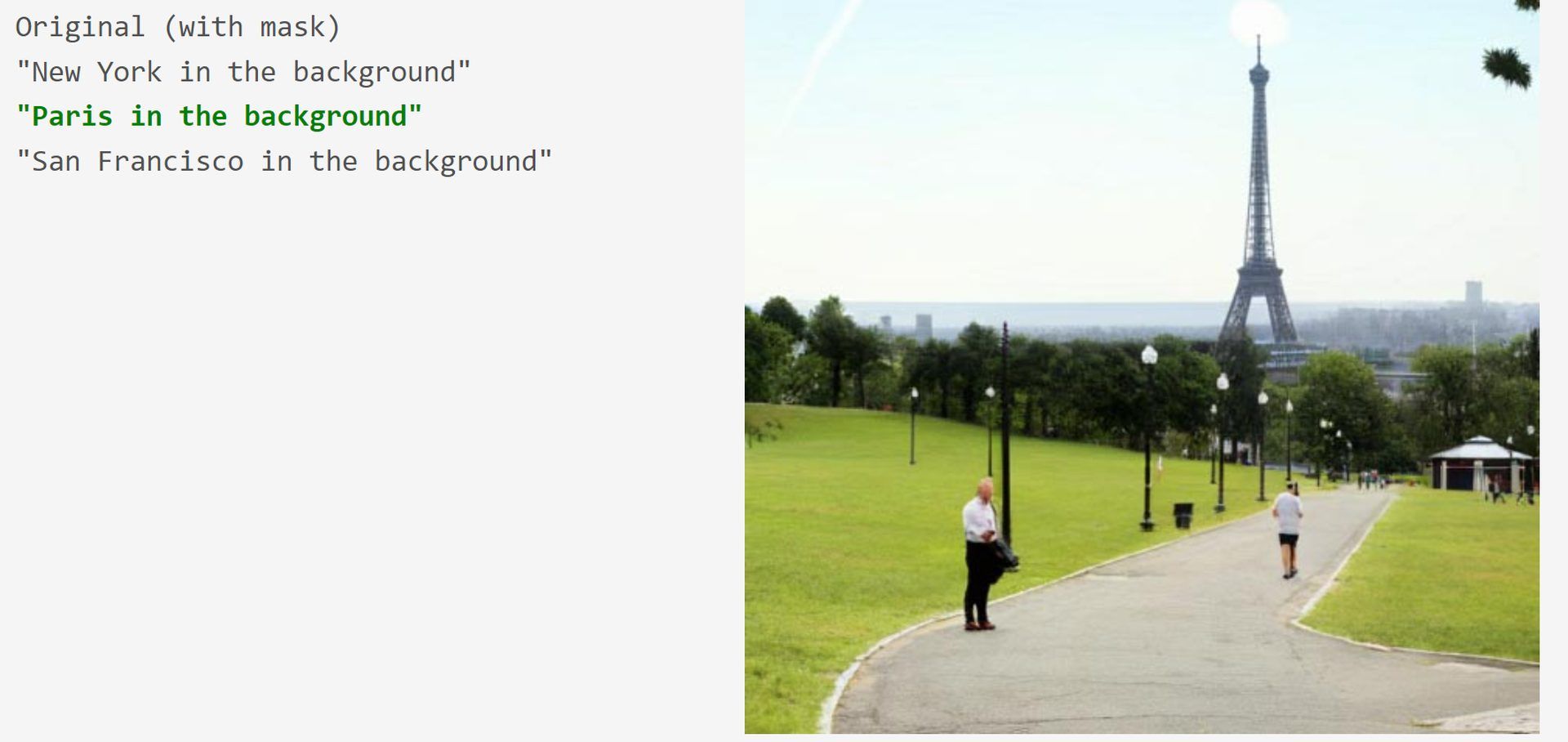
Google Muse AI model details
Below you find Google Muse AI’s training pipeline:
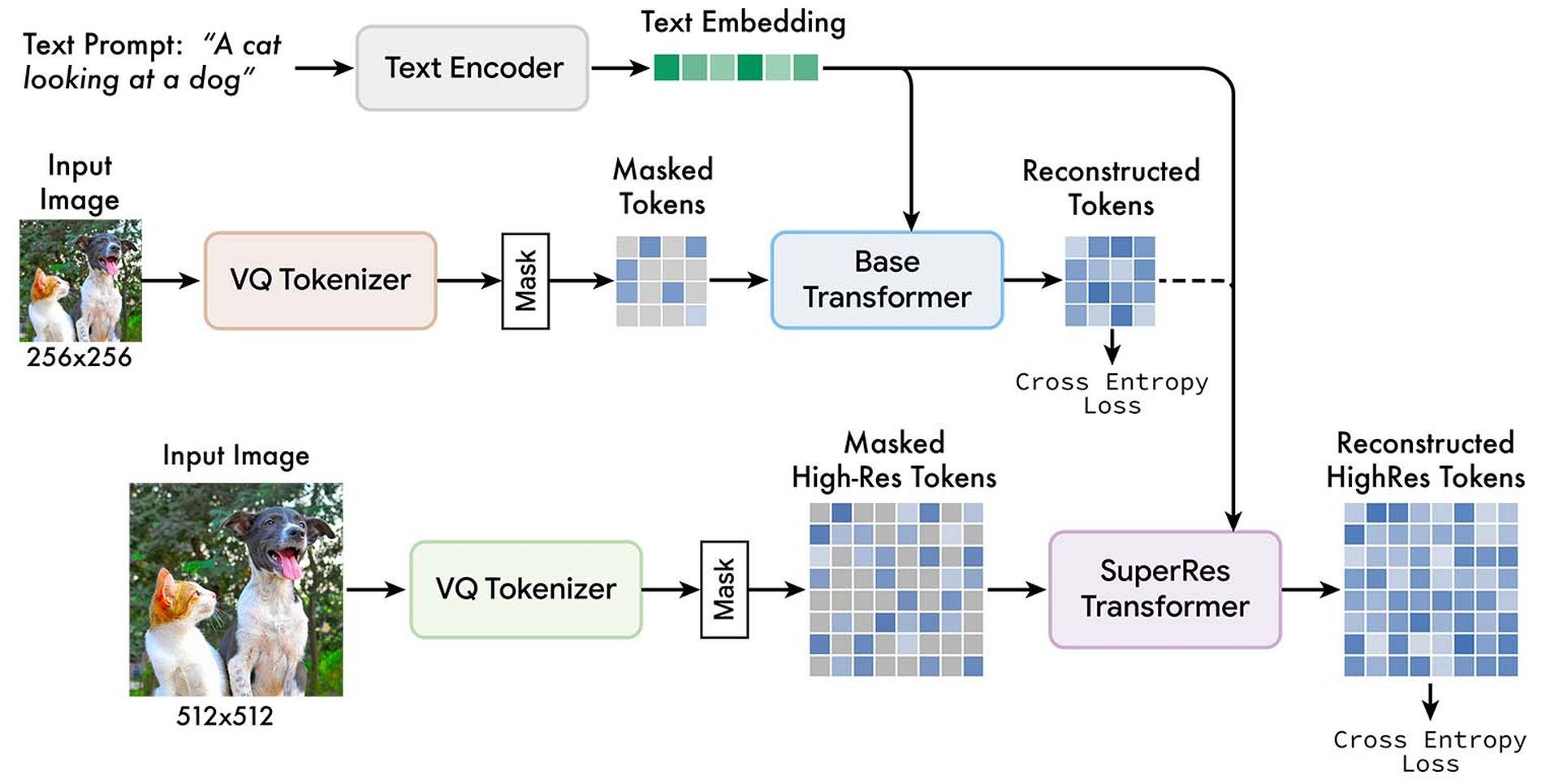
The Google team uses two separate VQGAN tokenizer networks, one for low-quality photos and one for high-resolution images. The unmasked tokens and T5 text embeddings are used to train low-resolution (“base”) and high-resolution (“superres”) transformers to predict the masked tokens.
For more detailed information about Google Muse AI, click here.
Are you wondering how your room will be in cyberpunk style? Try Interior AI
Other AI tools we have reviewed
We have already explained some of the best AI tools like Meta’s Galactica AI, Notion AI, Chai, NovelAI, ChatGPT, Caktus AI, Uberduck AI, MOVIO AI, Make-A-Video, and AI Dungeon. Do you know there are also AI art robots? Check the Ai-Da.
Are you into AI image generation? You can try these tools:
- MyHeritage AI Time Machine,
- Reface app
- Dawn AI
- Lensa AI
- Meitu AI Art
- Stable Diffusion
- DALL-E 2
- Midjourney
- DreamBooth AI
- Wombo Dream
- NightCafe AI
- QQ Different Dimension Me
Don’t be scared of AI jargon; we have created a detailed AI glossary for the most commonly used artificial intelligence terms and explain the basics of artificial intelligence as well as the risks and benefits of artificial intelligence.






