What is generative AI, and how will it change the future? Over two billion dollars have already been invested in generative artificial intelligence, a rise of 425 percent since 2020. Machine learning is one of the more popular applications of generative artificial intelligence. This technique can be used to generate new images, videos, or text based on training data. ChatGPT, DALL-E 2, and Bing AI are just some of the popular examples of generative AI tools.
Are you new to artificial intelligence? Don’t worry; there’s still time to hop on the AI train. Don’t be scared of AI jargon; we have created a detailed AI glossary for the most commonly used artificial intelligence terms and explain the basics of artificial intelligence as well as the risks and benefits of artificial intelligence. Are generative AI tools risky too? Keep reading and find out.
What is generative AI?
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a subfield that focuses on creating new data rather than only analyzing and classifying already-existing data. The term generative artificial intelligence (AI) refers to machine learning algorithms that are able to derive new meaning from existing content, such as text, images, and code. The leading generative AI tools include DeepMind’s Alpha Code (GoogleLab), ChatGPT, GPT-3.5, DALL-E, MidJourney, Jasper, and Stable Diffusion.
What will be the most important technology over the next 50 years?
Emad believes it's Generative AI. I think it's age-reversal technology. What do you think? pic.twitter.com/ZLBBu65fkX
— Peter H. Diamandis, MD (@PeterDiamandis) February 8, 2023
The technology that allows the generation of new content using pre-existing text, audio files, or images is known as generative artificial intelligence (AI). Through the use of generative artificial intelligence, computers are able to recognize the underlying pattern associated with the input and generate equivalent content.
Generative AI techniques
There are 3 generative AI techniques:
Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
GANs are comprised of two neural networks: a generator and a discriminator. These neural networks compete with one another to achieve a state of equilibrium between the two networks
Transformers
Transformers, like GPT-3, LaMDA, and Wu-Dao, can simulate cognitive attention and differentially estimate the relevance of the various sections of the input data. They are taught some classification tasks, taught how to generate words or images from enormous databases, and trained to understand the language or the image.
Variational auto-encoders
While the encoder transforms the input into a compressed code, the decoder takes this code and reproduces the original information.
What do generative AI tools mean for us?
Machines’ ability to create sensical and attractive things is just beginning to develop. Generative AI describes situations in which the computer creates something new rather than evaluating something already existing.

Generative AI tools are well on their way to becoming quicker and more cost-effective than what people can generate by hand and, in some circumstances, superior to what they produce. Every sector that relies on humans to produce original work, such as social media and gaming, advertising and architecture, coding and graphic design, product design and law, and marketing and sales, is ripe for innovation. However, generative AI could enable better, faster, and cheaper production across various end markets. This is because AI may be totally supplanted by certain functions, while others are more likely to prosper from a tight iterative creative cycle between humans and machines. The hope is that generative AI will bring the marginal cost of creation and knowledge work closer and closer to zero, which would result in enormous labor productivity and economic value, as well as a market cap that is proportional to those two factors.
Knowledge work and creative labor, two of the categories that generative AI seeks to improve, collectively employ billions of people. Generative artificial intelligence has the potential to make these workers at least 10 percent more efficient and/or creative. This means that they become not just quicker and more efficient but also more capable than they were before. Therefore, generative artificial intelligence has the potential to generate economic value in trillions of dollars.
AI guides: Learning how to use AI is a game changer
Generative AI applications: It’s already with us
Generative AI applications rapidly expand and cover an extremely wide range of applications. They can take in a variety of content types, including photos, extended text formats, emails, content from social media platforms, voice recordings, structured data, and program code. They are even capable of producing fresh content, translations replies to inquiries, analysis of sentiment, summaries, and even films. These universal content engines have a lot of potential uses in business. Currently, marketing applications are some of the most typical ways that generative AI is used. There is a possibility that generative artificial intelligence will affect the fields of medicine and life sciences in the not-too-distant future, particularly in the areas of disease diagnosis and the discovery of new treatments.
For now: The following is a list of some of the generative AI applications that you can see with your own eyes in your everyday life:
- Copywriting: Language models are ideally suited for use in applications such as the ever-increasing demand for personalized web and email content to fuel sales and marketing efforts as well as customer assistance
- Writing assistants: An artificial intelligence writing assistant is any piece of software that is intended to speed up the process of writing content on its own. This includes AI copywriting tools like Copysmith that provide a broad list of writing features and solutions that serve a single purpose, like Grammarly.
- Code generation: Several generative AI tools can generate code that is comparable to or even superior to that which humans create. This is an important step forward and demonstrates how AI may be used to write better code more quickly.
- Art generation: AI art generators are pieces of software that autonomously create artwork by employing various forms of artificial intelligence. These programs often come in one of two flavors: either text-to-image or image-to-image. Text-to-image generators can produce one-of-a-kind images depending on the text input provided by a user, which is also referred to as a prompt in many contexts. People already fall in love with generative AI images.
- Gaming: The term “AI” in the gaming industry refers to responsive and adaptive experiences. These AI-driven interactive experiences are typically generated by non-player characters, also known as NPCs, that behave in a clever or creative way as if a human game player was directing them. The AI determines the behavior of non-player characters (NPCs) in the game environment.
- Media/Advertising: AI is the simulation of human intellect in machines. These computers are built to think like humans and mimic their actions based on the information that is provided to them. Hence AI in advertising refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines. They use historical data to gain insight from previous experiences and apply that insight while making decisions for the future.
- Design: Because of its enhanced speed and efficiency, designers who work with AI can generate designs at a lower cost and in a shorter amount of time. The speed with which artificial intelligence can assess massive volumes of data and make recommendations for design changes will be the source of its power.
- Social networks: AI technology is an integral part of many major social networks, such as the ones you use daily and the marketing that takes place on those sites. Generative AI images also used in social networks.
If you have been wondering which generative AI tools are compatible with these applications, you will be pleased to learn that the answer is now ready.
Best generative AI tools
Almost every day, a new tool, model, or feature pops up and changes our lives, like ChatGPT, and we have already reviewed some of the best ones:
- Google Bard AI
- Bing AI
- Chinchilla
- Notion AI
- Google Apprentice Bard
- Chai
- NovelAI
- Caktus AI
- AI Dungeon
- YouChat
- Neeva AI
- Fake name generators
Do you want to learn how to use ChatGPT effectively? We have some tips and tricks for you without switching to ChatGPT Plus! AI prompt engineering is the key to limitless worlds, but you should be careful; when you want to use the AI tool, you can get errors like ChatGPT is at capacity right now or “Too many requests in 1 hour try again later” error. Yes, they are really annoying errors, but don’t worry; we know how to fix them.
- Text-to-image AI tools
While there are still some debates about artificial intelligence-generated images, people are still looking for the best AI art generators and love generative AI images. Will AI replace designers? Keep reading and find out.
Do you want more tools? Check out the best free AI art generators.
Generative AI images
As you see above, most of the popular Generative AI tools are about image generation. generative AI tools take text input and use it as the basis for generating visuals in two, three, and even four dimensions. Here are some examples of generative AI images:

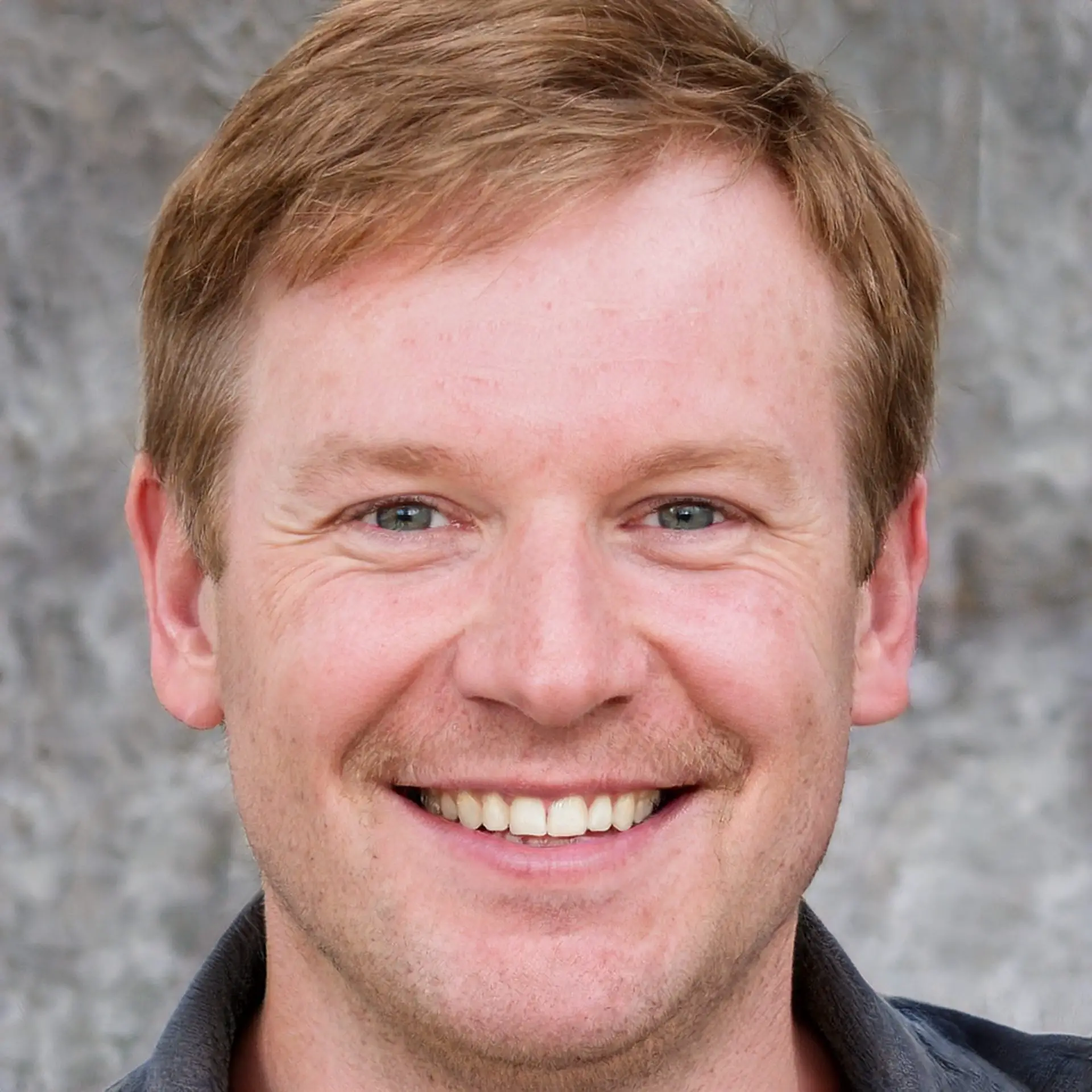
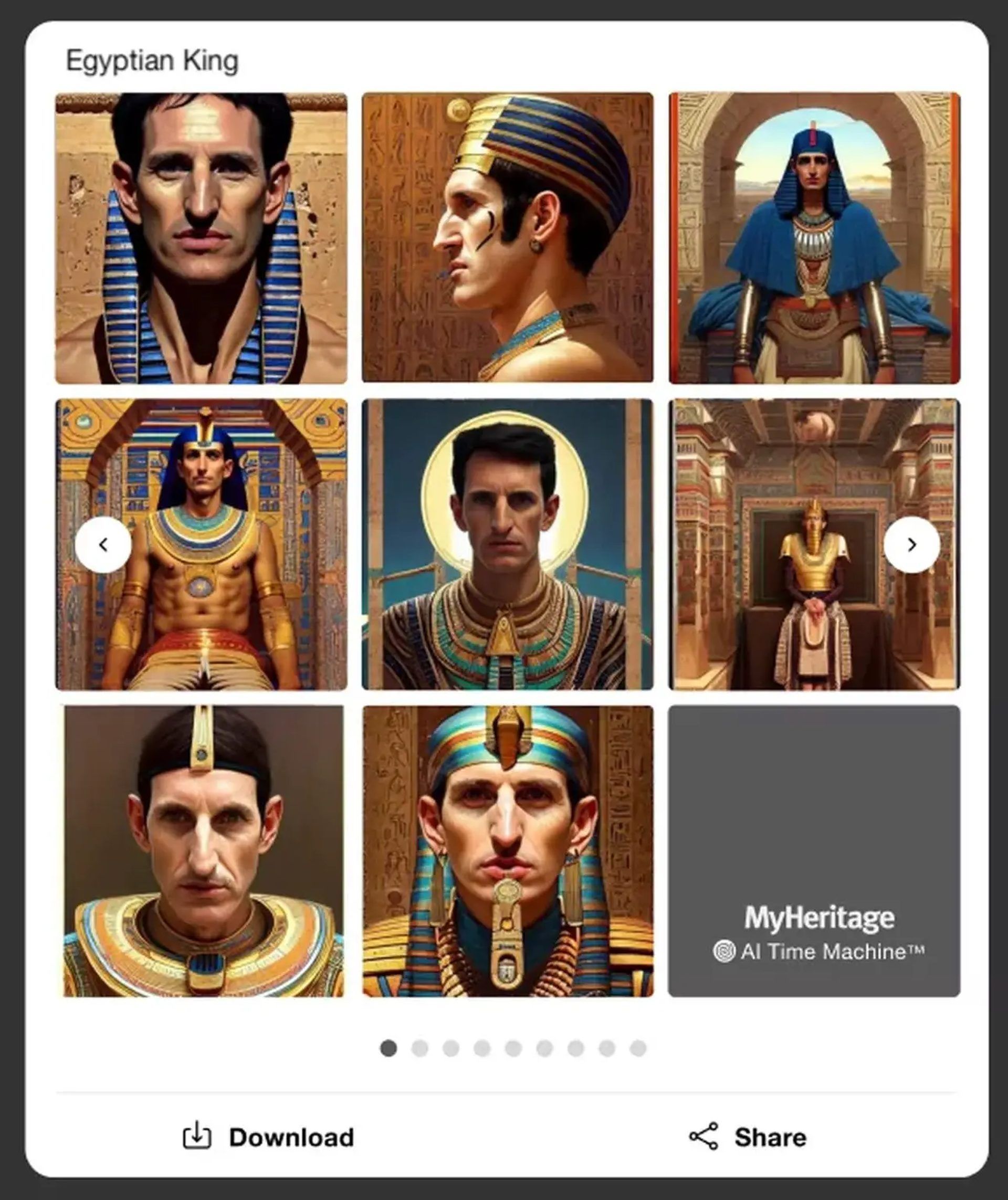
Generative AI can create hyper-realistic human portraits. Below you can find a generative AI example that looks like a real photo.

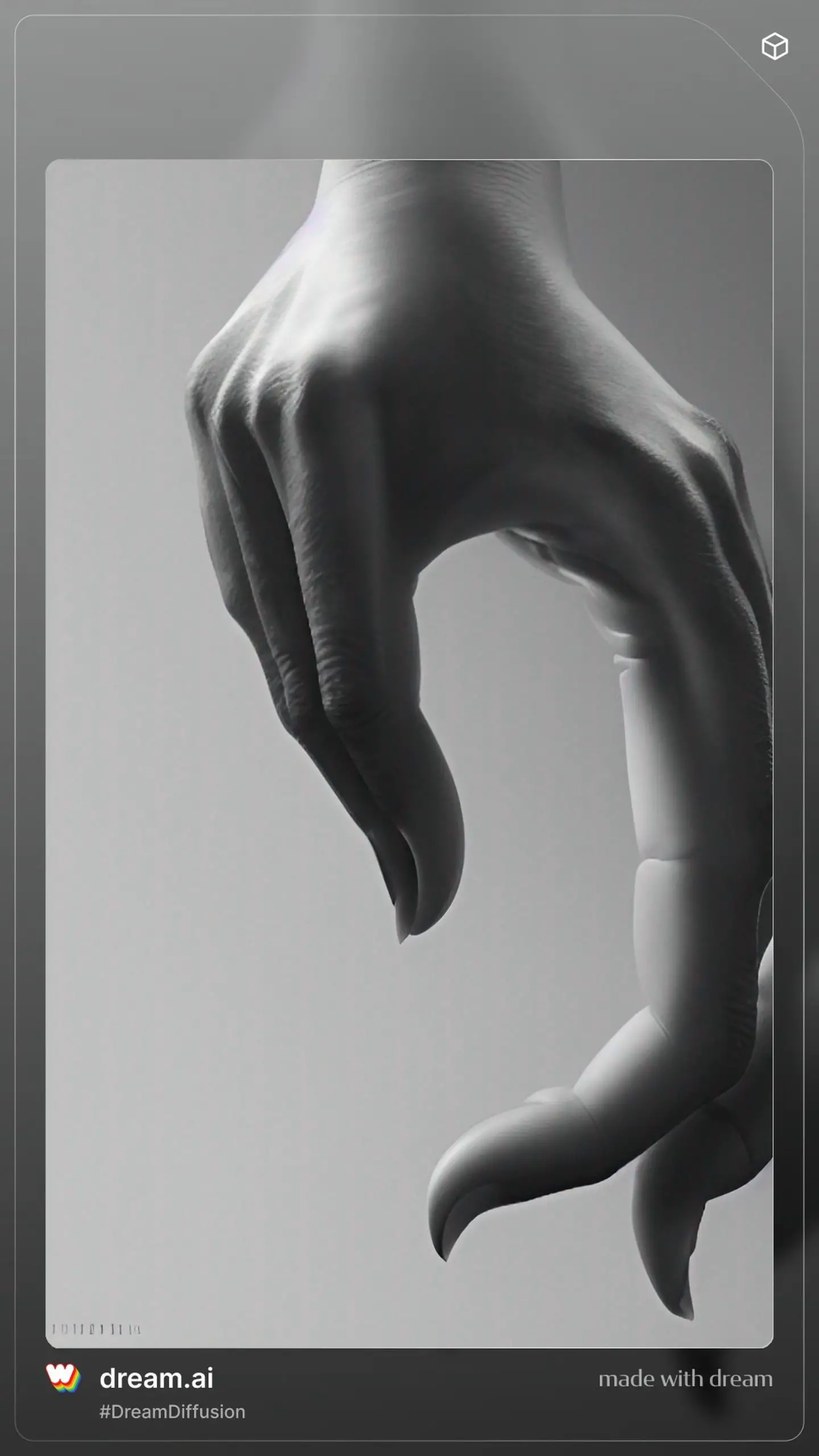
Do you know although generative AI images are so successful, AI can’t draw hands? AI drawing hands is one of the biggest unsolved issues of AI.
Below you can find a generative AI example that did not produce the desired result.

One of the most popular types of AI image generation is making avatars. For generative AI examples, TikTok is one of the most popular place to share.
@dawnaiapp
With generative AI tools, you can easily be an astronaut, a 19th-century lord or lady, a medieval knight, or an Egyptian pharaoh!
Generative AI images are not the only examples of artificial intelligence.
Generative AI examples
Any algorithm or model that uses AI to produce an entirely new attribute is considered to use generative AI. At this moment, the most notable examples are ChatGPT and DALL-E, in addition to any of their potential replacements. One such illustration of this would be Google’s unreleased AI text-to-music generator known as MusicLM. Google’s Bard is yet another project that is currently in development.
The rise in popularity of generative AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and DALL-E has led to more attention being paid to the phrase “generative AI,” which describes these types of systems. Both the conversational chatbot and the AI image generator use generative artificial intelligence to produce new content in a matter of seconds. This new content can take the form of computer code, essays, emails, social media captions, images, poems, or raps, among other things. This rapid production captures people’s attention.
Generative AI companies
The year 2022 set a new high watermark for investment in the field of generative AI companies, with equity capital surpassing $2.6 billion over 110 separate agreements, according to CB Insights.
The following generative AI companies closed the year with the largest funding rounds:
- Anthropic ($580M Series B)
- Inflection AI ($225M Series A)
- Cohere ($125M Series B)
- Jasper ($125M Series A)
There have been six generative AI companies in the sector that have achieved unicorn status (worth over $1 billion each), including the following:
- OpenAI
- Hugging Face
- Lightricks
- Jasper
- Glean
- Stability AI
As the field of artificial intelligence (AI) continues to advance, we are now moving into uncharted territory in the form of a new frontier. Gartner anticipates that by the year 2025, at least 30 percent of all newly found materials and pharmaceuticals will originate from generative AI models.
We are already seeing tools like GPT-3 and ChatGPT leverage AI in creative text and natural language ways. As a result, it is becoming increasingly difficult to differentiate between content and answers created by humans and AI-generated. These new chat innovations will start to impact various knowledge worker roles once highly repeatable processes, in which humans don’t have a lot of variety in their communication responses, are involved. Some examples of these highly repeatable processes include call centers, administrative functions, routine medical questions, etc.
Disadvantages of generative AI
Generative AI models collect a large quantity of content from across the internet, use the data they were trained on to generate predictions, and then produce an output in response to a prompt that the user inputs. These forecasts are derived from the facts, but there is no warranty that they will be accurate in the future. The responses may also contain biases inherent in the content the model has consumed from the internet; however, there is typically no way to know whether or not this is the case. There are a lot of generative AI examples that shows the situation to us.
These models do not necessarily know whether or not the things they produce are correct, and we have no means of understanding where the information has come from or how it has been processed by the algorithms used to generate content. There are numerous cases of chatbots offering erroneous information or simply making stuff up to fill in the gaps. Some of these generative AI examples include the following: It would be unwise, particularly in the short term, to rely on the information or content that is produced by generative AI, even though the outputs can be engaging and entertaining in their own right.
Concerns of a legal and ethical nature may arise in connection with generative AI tools. One of these is the capacity to readily create “deepfakes,” which are computer-generated pictures or videos that give the impression of being realistic but are actually fake or deceptive. In addition, generative artificial intelligence poses problems regarding what constitutes original and proprietary work, and it may considerably impact the ownership of content.
Did you think it was over? They are not the only challenges of generative AI; we add titles to the list, such as:
- Security
- Overestimation of capabilities
- Unexpected outcomes
- Data privacy
I’m cropping these for privacy reasons/because I’m not trying to call out any one individual. These are all Lensa portraits where the mangled remains of an artist’s signature is still visible. That’s the remains of the signature of one of the multiple artists it stole from.
A 🧵 https://t.co/0lS4WHmQfW pic.twitter.com/7GfDXZ22s1
— Lauryn Ipsum (@LaurynIpsum) December 6, 2022
Despite its limitations and challenges, the generative AI sector is impressively big.
Generative AI market size: 2023
The generative AI market size reached 10.3 billion US dollars in 2022, and it is anticipated to reach $53.9 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.2%.
Generative AI images and chatbots are some of the generative AI examples that keep getting bigger in the market daily.






