Artificial intelligence is no longer fiction and the role of AI databases has emerged as a cornerstone in driving innovation and progress. An AI database is not merely a repository of information but a dynamic and specialized system meticulously crafted to cater to the intricate demands of AI and ML applications. With the capacity to store, organize, and retrieve data efficiently, AI databases provide the scaffolding upon which groundbreaking AI models are built, refined, and deployed.
As the complexity of AI and ML workflows deepens, the reliance on large volumes of data, intricate data structures, and sophisticated analysis techniques becomes more pronounced. Herein lies the crux of the AI database’s significance: it is tailored to meet the intricate requirements that underpin the success of AI and ML endeavors. No longer confined to traditional databases, AI databases are optimized to accommodate a spectrum of data types, each uniquely contributing to the overarching goals of AI—learning, understanding, and predictive analysis.
But which AI database tools can you rely on for your artificial journey into today’s technology? Let’s take the first step of a successful AI initiative together.

What is an AI database?
An AI database is a specialized type of database designed to support the storage, management, and efficient retrieval of data used in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications. These databases are engineered to accommodate the unique requirements of AI and ML workflows, which often involve large volumes of data, complex data structures, and sophisticated querying and analysis.
AI databases are optimized to handle various types of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, that are essential for training and deploying AI models. The types of data mentioned in the context of AI databases refer to different formats in which information is stored and organized. These formats play a significant role in how data is processed, analyzed, and used to develop AI models.
Structured data is organized in a highly organized and predefined manner. It follows a clear data model, where each data entry has specific fields and attributes with well-defined data types.
Examples of structured data include data stored in traditional relational databases, spreadsheets, and tables. In structured data, the relationships between data points are explicitly defined, making it easy to query and analyze using standardized methods. For AI applications, structured data can include numerical values, categorical labels, dates, and other well-defined information.
Semi-structured data is more flexible than structured data but still has some level of organization. Unlike structured data, semi-structured data doesn’t adhere to a strict schema, meaning that different entries can have different sets of attributes. However, there is usually some consistency in the way the data is organized.
Semi-structured data is often represented using formats like JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), XML (eXtensible Markup Language), or key-value pairs. This type of data is common in web data, sensor data, and data obtained from APIs. In AI, semi-structured data might include text with associated metadata or data with varying levels of structure.
Unstructured data lacks a predefined structure or format. It is typically more complex and challenging to process than structured or semi-structured data. Unstructured data includes text, images, audio, video, and other data types that don’t neatly fit into rows and columns.
In AI applications, unstructured data can be vital for tasks such as natural language processing, image recognition, and sentiment analysis. Analyzing unstructured data often involves using techniques like machine learning to extract meaningful patterns and insights from the raw information.

What makes AI databases different from traditional databases?
They provide the foundation for data preprocessing, feature extraction, model training, and inference.
Several key features set AI databases apart from traditional databases:
- Scalability: AI databases are designed to scale horizontally and vertically, enabling them to handle the substantial amounts of data required for training complex models. They often leverage distributed computing techniques to manage and process data efficiently
- Data diversity: AI databases can handle a wide variety of data types, including text, images, audio, video, and sensor data. This versatility is crucial for training models that require multi-modal data sources
- Complex queries: AI databases support advanced querying capabilities to enable complex analytical tasks. This may involve querying based on patterns, relationships, and statistical analysis required for ML model development
- Parallel processing: Given the computational demands of AI and ML tasks, AI databases are optimized for parallel processing and optimized query execution
- Integration with ML frameworks: Some AI databases offer integration with popular machine learning frameworks, allowing seamless data extraction and transformation for model training
- Feature engineering: AI databases often provide tools for data preprocessing and feature engineering, which are crucial steps in preparing data for ML tasks
- Real-time data ingestion: Many AI applications require real-time or near-real-time data processing. AI databases are equipped to handle streaming data sources and provide mechanisms for timely ingestion and analysis
- Metadata management: Managing metadata related to data sources, transformations, and lineage is crucial for ensuring data quality and model reproducibility
- Security and privacy: AI databases need to ensure robust security mechanisms, particularly as AI applications often involve sensitive data. Features like access controls, encryption, and anonymization may be implemented
What are the top 10 AI databases in 2023?
The selection of a suitable AI database is a crucial consideration that can significantly impact the success of projects.
The diverse options of available databases offer a range of options, each tailored to meet specific requirements and preferences.
Redis
Redis stands out as an open-source, in-memory data structure that has gained recognition for its versatility and robust feature set. It boasts the ability to support various data types, ranging from simple strings to more complex data structures, enabling developers to work with diverse data formats efficiently.
Furthermore, Redis encompasses a rich spectrum of functionalities, including support for transactions, scripting capabilities, and data replication, which enhances data durability and availability.
PostgreSQL
As an open-source object-relational AI database system, PostgreSQL has earned its reputation for its unwavering commitment to data integrity and advanced indexing mechanisms. Its support for various data types makes it a versatile choice, accommodating a wide array of data structures.
With a strong emphasis on ACID compliance (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability), PostgreSQL is well-equipped to handle complex data workloads with the utmost security and reliability.
MySQL
MySQL, a renowned open-source relational AI database management system, has maintained its popularity for its strong security measures, scalability, and compatibility. It seamlessly accommodates structured and semi-structured data, making it adaptable to a diverse range of applications.
MySQL’s reliability and performance have made it a favored choice in various industries, and its open-source nature ensures a thriving community and continuous development.
Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra has emerged as a highly scalable NoSQL database, favored by major platforms like Instagram and Netflix. Its automatic sharding and decentralized architecture empower it to manage vast amounts of data efficiently.
This makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring high levels of scalability and fault tolerance, as it effortlessly accommodates the demands of modern data-driven initiatives.
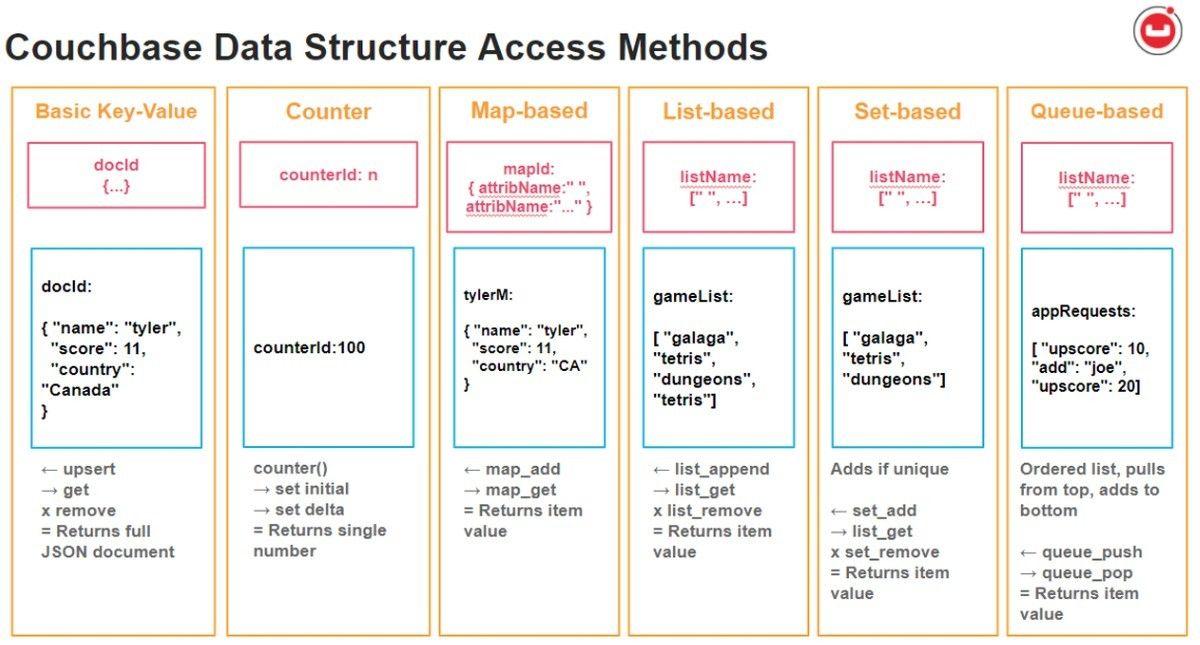
Couchbase
Couchbase is an open-source distributed engagement database that offers a potent combination of high availability and sub-millisecond latencies. Beyond its performance merits, Couchbase also integrates Big Data and SQL functionalities, positioning it as a multifaceted solution for complex AI and ML tasks.
This blend of features makes it an attractive option for applications requiring real-time data access and analytical capabilities.
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch, built on the foundation of Apache Lucene, introduces a distributed search and analytics engine that facilitates the extraction of real-time data insights. Its capabilities prove invaluable in applications demanding rapid data retrieval and analytics, enabling informed decision-making.
With its real-time querying prowess, Elasticsearch contributes significantly to enhancing AI and ML workflows.
Google Cloud Bigtable
Google Cloud Bigtable distinguishes itself as a distributed NoSQL AI database offering robust scalability, low latency, and data consistency. These features make it particularly adept at handling high-speed data access requirements.
However, it’s worth noting that while Google Cloud Bigtable excels in performance, its pricing complexity may require careful consideration during implementation.
See how Google Cloud Bigtable works in the video by Google Cloud Tech below.
MongoDB
MongoDB‘s prominence lies in its flexible, document-oriented approach to data management. This attribute, coupled with its scalability capabilities, makes it an attractive choice for handling unstructured data.
Developers seeking to manage complex data structures and accommodate the dynamic nature of AI and ML projects find MongoDB’s features well-aligned with their needs.
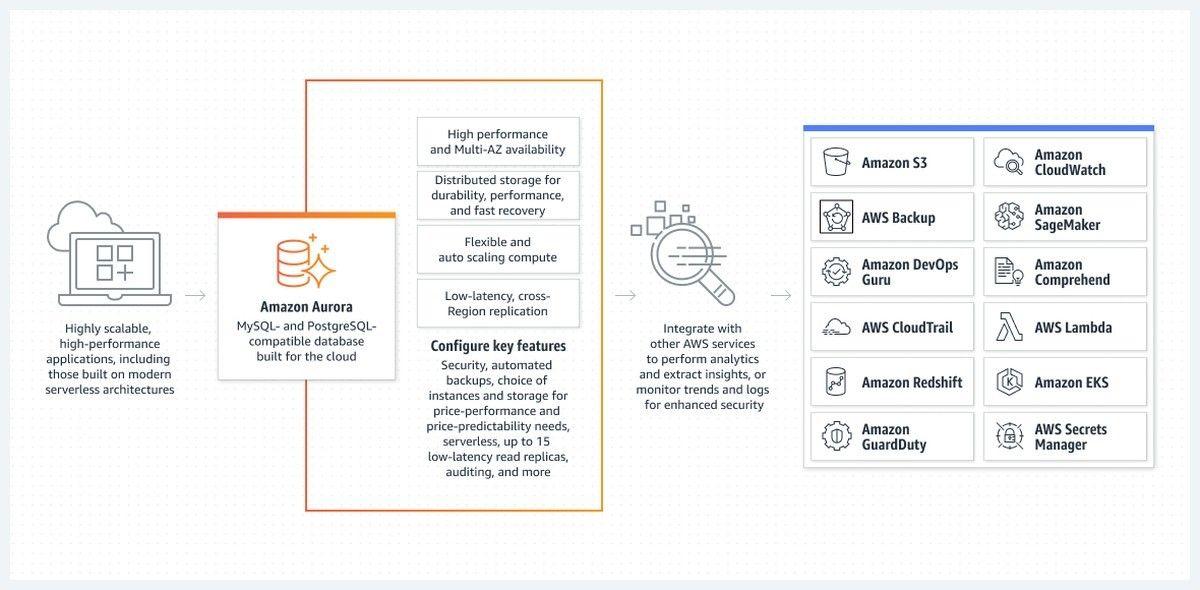
Amazon Aurora
Amazon Aurora, a high-performance relational database, offers compatibility with MySQL and PostgreSQL. Its ability to scale seamlessly and robust security features and automatic backup mechanisms position it as a compelling option for AI and ML applications.
Organizations leveraging Amazon Aurora benefit from its efficient handling of complex data workloads.
Chorus.ai
Chorus.ai takes a specialized approach by targeting client-facing and sales teams. It provides an AI assistant designed to enhance note-taking processes. As businesses strive to streamline interactions and gather insights from customer engagements, Chorus.ai’s AI assistant plays a pivotal role in capturing vital information and fostering efficient communication.
How to choose the right AI database for your needs
The key to selecting the right AI database lies in aligning the database’s features and capabilities with the specific requirements of the project at hand. By carefully evaluating factors such as scalability, security, data consistency, and support for different data types and structures, developers can make accurate decisions that contribute to the success of their AI and ML endeavors.
To choose the right AI database, start by clearly defining your project’s requirements. Consider factors such as the volume of data you’ll be dealing with, the complexity of your data structures, the need for real-time processing, and the types of AI and ML tasks you’ll be performing.
Once you have decided your requirements for the selection of an AI database, evaluate the types of data you’ll be working with—structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. Ensure that the AI database you choose can efficiently handle the variety of data your project requires.
Don’t forget to consider the scalability needs of your project. If you expect your data to grow significantly over time, opt for a database that offers horizontal scaling capabilities to accommodate the increased load.
Assess the performance metrics of the AI database. For real-time applications or high-speed data processing, choose a database that offers low latency and high throughput.
Once you have done that, review the querying and analytical capabilities of the database. Depending on your project’s requirements, you may need advanced querying features to extract insights from your data.
If you’re planning to use specific machine learning frameworks, consider databases that offer integration with those frameworks. This can streamline the process of data extraction and transformation for model training.

Data security is also paramount, especially if your project involves sensitive information. Ensure the AI database you are going to choose offers robust security features, including access controls, encryption, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Evaluate the user-friendliness of the database. An intuitive interface and user-friendly management tools can simplify data administration and reduce the learning curve.
Make sure that you also consider the size and activity of the user community surrounding the database. A strong community often indicates ongoing development, support, and a wealth of resources for troubleshooting.
Also, look for case studies and examples of how the AI database has been successfully used in projects similar to yours. This can provide insights into the database’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
By carefully considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can identify the AI database that best aligns with your project’s needs and goals. Remember that selecting the right database is a crucial step in building a solid foundation for successful AI and ML endeavors.
Featured image credit: Kerem Gülen/Midjourney.






