AI computers are real now, and they are rapidly changing the world around us and already being used in a wide range of applications in various sectors.
The capacity of computers to think, learn, make decisions, and be creative are all examples of what we mean when we talk about artificial intelligence (AI). Rapid progress in AI has been made in recent years due to an abundance of data, high-powered processing hardware, and complex algorithms. One of the most fascinating uses of AI is in the creation of AI computers, which are able to execute a wide range of AI-based programs and activities without any human interaction.
What is an AI computer?
An AI computer, also known as an artificial intelligence computer or AI PC, is a computer system that is specifically designed to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning. AI computers can be programmed to perform a wide range of tasks, from natural language processing and image recognition to predictive analytics and decision-making. These computers typically use machine learning algorithms and other AI techniques to improve their performance over time, allowing them to become more accurate and effective at their tasks. Some examples of AI computers include chatbots, autonomous vehicles, and recommendation engines used by online retailers.
AI computers can be classified into two main types:
- General-purpose
- Specialized
General-purpose AI computers are designed to handle a wide range of AI tasks, such as natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and machine learning. They can also switch between different tasks and learn from new data. Examples of general-purpose AI computers include Google’s TPU (Tensor Processing Unit), Nvidia’s DGX (Deep Learning System), and IBM’s Watson.
Specialized AI computers are optimized for specific AI domains or applications, such as gaming, robotics, or healthcare. They have customized hardware and software architectures that can perform faster and more efficiently than general-purpose AI computers for their target tasks. Examples of specialized AI computers include DeepMind’s AlphaGo (a system that defeated the world champion of Go), Boston Dynamics’ Spot (a four-legged robot that can navigate complex terrains), and IBM’s Watson Health (a system that can analyze medical data and provide diagnosis and treatment recommendations).
AI computers have many benefits and challenges for society. On the one hand, they can enhance human capabilities, improve productivity, solve complex problems, and create new opportunities. On the other hand, they can also pose ethical, social, legal, and security risks, such as displacing human workers, violating privacy, causing bias and discrimination, and creating malicious or rogue AI agents. Therefore, it is important to develop AI computers with responsibility, accountability, transparency, and human values in mind.
To provide a more comprehensive explanation of the term “AI computer,” we should also refer to AI computing.
What is AI computing?
The term “AI computing” describes the use of computers and software algorithms for intellectually demanding activities, including learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. In order to mimic the human brain’s pattern recognition, learning, and adaptability, AI computing systems are built with these characteristics in mind.
Artificial intelligence (AI) computing uses machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and other methods to enable computers to carry out operations that were once exclusively the purview of humans. Image and speech recognition, autonomous cars, and medical diagnostics are just a few of the areas where AI computing’s processing capacity and sophisticated algorithms have facilitated significant advances.
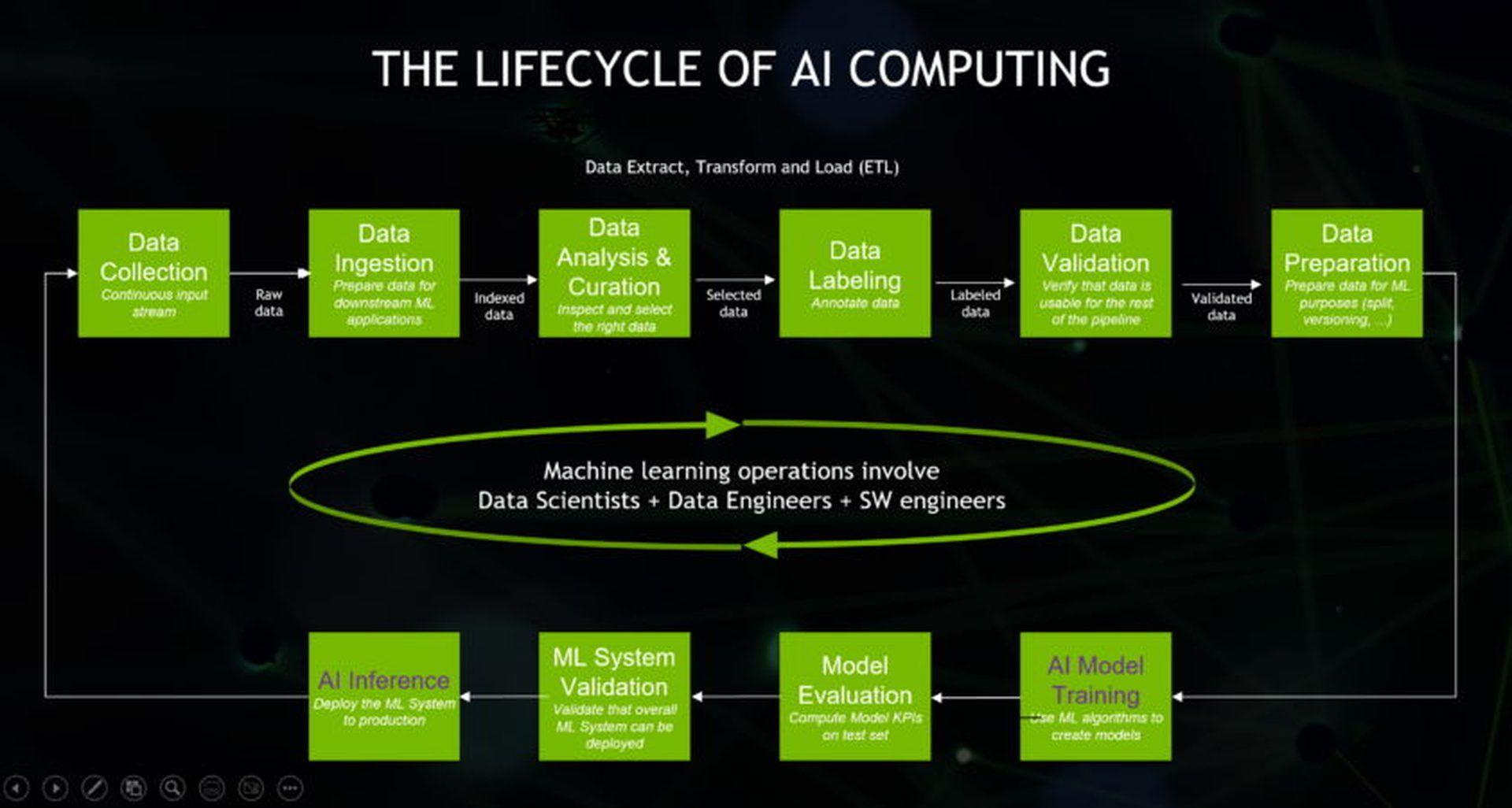
According to Nvidia, the lifecycle of AI computing is explained below.
If AI computing keeps improving, it might completely alter numerous sectors and the way we live and work, and it’s already started.
AI computer examples
Here are some of the best AI computer examples in real life:
- Personal assistants: Devices like Amazon’s Alexa, Google Home, and Apple’s Siri are examples of AI computers that use natural language processing to respond to voice commands and provide information or perform tasks.
- Self-driving cars: Companies like Tesla and Google are working on creating fully autonomous vehicles that use a combination of sensors, cameras, and machine learning algorithms to navigate roads and make decisions in real time.
- Fraud detection: Financial institutions use AI computers to analyze vast amounts of data and detect patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity. These systems can flag suspicious transactions and help prevent fraud before it occurs.
- Medical diagnosis: AI computers can analyze medical data such as X-rays, and CT scans to help diagnose illnesses and identify potential health risks.
- Personalized recommendations: Online retailers and streaming services use AI computers to analyze user data and recommend products or content based on a user’s previous behavior and preferences.
There are just some examples from the early AI computer era. So what awaits us in the future? Now, AI can think, but what will happen when it truly sees?
AI computer vision
The goal of computer vision, a subfield of AI, is to enable computers and other systems to infer important details from digital photos, videos, and other visual inputs and then act upon or propose those details. Although AI makes it possible for machines to reason, computer vision makes it possible for them to see, watch, and comprehend.
Human vision and computer vision are functionally equivalent, with the exception that human eyesight is more developed. The human visual system has had a lifetime to learn how to distinguish between things, judge their distance, detect motion, and spot inconsistencies in a picture.
Using cameras, data, and algorithms in place of retinas, optic nerves, and a visual brain, computer vision educates robots to carry out these tasks in a significantly shorter amount of time. Since it can evaluate hundreds of items or processes per minute, a system trained to examine products or supervise a manufacturing asset can soon outpace human skills.
Energy and utilities, manufacturing, and the automobile industry are just a few of the expanding markets for computer vision technology. By 2022, it is projected to be worth $48.6 billion.

Several well-known applications of computer vision are listed below:
- Image classification: A computer capable of doing image classification can tell what it’s looking at (a dog, an apple, a human face, etc.). In particular, it may confidently assert that an input image belongs to a specified category. It might be used by a social networking platform, for instance, to filter out offensive photos that people post.
- Object detection: Images can be classified into groups so that object detection can search for and catalog instances of those groups inside a given picture or video. Finding broken parts on the production line or malfunctioning machines that need servicing are only two examples.
- Object tracking: When an item is discovered, it may be followed using object tracking. Sequential photos or live video streams are common tools for carrying out this operation. To avoid accidents and follow traffic regulations, autonomous vehicles, for instance, need not only to recognize and categorize moving things like people, other vehicles, and road infrastructure but also follow them as they move.
- Content-based image retrieval: In contrast to traditional image retrieval methods, which rely on metadata tags, content-based image retrieval employs computer vision to search, explore, and retrieve pictures from large data warehouses based on the actual content of the images themselves. An alternative to manually annotating images for this activity is to use automated picture annotation. Digital asset management systems can benefit from these activities because they improve search and retrieval precision.
Why are AI computers rising?
There are several benefits of AI computers, including:
- Increased efficiency and productivity: AI computers can automate tasks that were previously performed by humans, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. This can save time and money for businesses, allowing them to focus on other tasks.
- Improved accuracy and precision: AI computers can perform tasks with a higher degree of accuracy and precision than humans, reducing the risk of errors and improving the quality of results.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI computers can analyze large amounts of data and provide insights that would be difficult for humans to detect. This can help decision-makers make more informed and data-driven decisions.
- Personalization: AI computers can personalize experiences for users by analyzing their preferences and behaviors. This can lead to more customized and satisfying experiences for users.
- Improved safety: AI computers can be used in situations that are too dangerous for humans, such as exploring deep-sea environments or handling hazardous materials.
- Cost savings: AI computers can perform tasks at a lower cost than humans, leading to cost savings for businesses and consumers.

Overall, AI computers have the potential to improve efficiency, accuracy, and safety in a wide range of industries and applications, leading to a better quality of life for individuals and society as a whole.
Disclaimer: AI computers are a relatively new topic. Because of that artificial intelligence tools was used for the definition of necessary terms at the time of writing.
Oh, are you new to AI, and everything seems too complicated? Keep reading…
AI 101
Are you new to AI? You can still get on the AI train! We have created a detailed AI glossary for the most commonly used artificial intelligence terms and explain the basics of artificial intelligence as well as the risks and benefits of AI. Feel free the use them. Learning how to use AI is a game changer! AI models will change the world.
AI tools we have reviewed
Almost every day, a new tool, model, or feature pops up and changes our lives, and we have already reviewed some of the best ones:
- Text-to-text AI tools
Do you want to learn how to use ChatGPT effectively? We have some tips and tricks for you without switching to ChatGPT Plus, like how to upload PDF to ChatGPT! However, When you want to use the AI tool, you can get errors like “ChatGPT is at capacity right now” and “too many requests in 1-hour try again later”. Yes, they are really annoying errors, but don’t worry; we know how to fix them. Is ChatGPT plagiarism free? It is a hard question to find a single answer. If you are afraid of plagiarism, feel free to use AI plagiarism checkers. Also, you can check other AI chatbots and AI essay writers for better results.
- Text-to-image AI tools
While there are still some debates about artificial intelligence-generated images, people are still looking for the best AI art generators. Will AI replace designers? Keep reading and find out.
- AI video tools
- AI presentation tools
- AI search engines
- AI interior design tools
- Other AI tools
Do you want more tools? Check out the best free AI art generators.






